As people in overall we focus more on what we lack of, where we are not perfect enough or where other people are “better” than us (whatever “better” means). Thinking about strengths, on things that we are really good at is not a first thing that come to our minds when we reflect on our professional development, have a quality conversation with our manager or we just think about next steps in our careers.
From my experience it’s strongly connected to the culture and/or country that we were raised within, because convictions about being strong or weak are very much there. As a person raised in Poland, where there’s always a need to prove that we are good, worthy or educated enough to be partners in any global professional context I can say that it’s a strong one. I know many people raised in different cultures and I can tell that there is a huge gap in mindset in this area, i.e. in compare to people raised in US.
But this article is not about cultural differences, even if the convictions we are going to talk about today are strongly tight to those. I would like to take us all on the journey of strengths.
Why we have a tendency to focus on the gaps, instead of focus on the strengths? Why we do it to ourselves when it’s so much easier to base on what we do really well? Let’s take a closer look at that.
What are strengths?
A strength is a superpower.
Strength is something that allows us to do things really easily. It’s natural, sometimes we do things even without any energy spent on the process. It can be automatic, with no conscious brain usage – like in the situation when we get into the car, we drive from point A and 20 minutes later we are at the point B without even noticing how we did it.
Strength is fun, interesting, we can be passionate about what it’s connected to or it can be linked to our values. When we use strengths everything seem easy, obvious – we are masters in our fields in that state, we can achieve more.
One of the best tools that you can use to learn more about your strengths is Gallup Strengths Finder (renamed recently to CliftonStrengths – but describing exactly the same thing). The concept states that we all have 34 talents in us, arranged in a different, unique order, depends on the person.
The whole journey starts with a questionnaire that name your TOP 5 talents you have inside yourself. There is an option to uncover the whole list of 34 at once – it’s more expensive and in my opinion it’s not necessarily needed when you start your journey with talents. You can always pay extra and uncover them without filling out a questionnaire again anytime you want. Your choice.
After going through the questions, you’ll get a short report with the list of your TOP 5 strengths – those are elements that you are a natural at, you don’t need to spend a lot of energy to reach to those buckets, it’s a part of yourself, like extending your own body and mind.
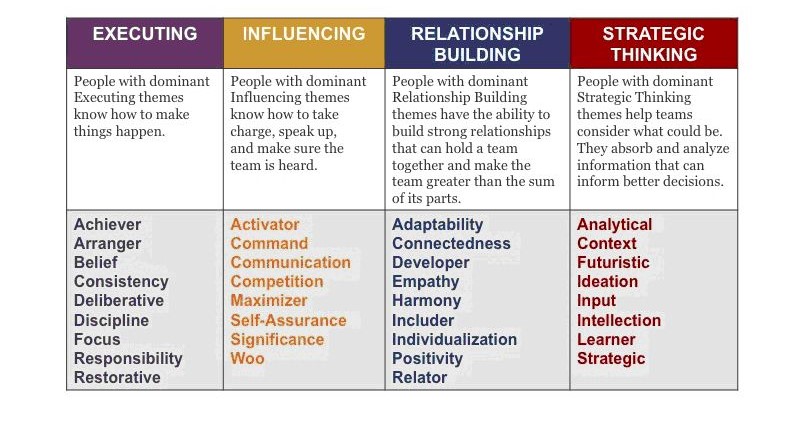
Talents are grouped into 4 categories: executing, influencing others (in a good way, with positive intention), relationship building and strategic thinking. Each strength has its own description to better understand what stays behind it. It’s a starting point for us to think how those elements fit to who we are in different situations at work and life.
How you can work with them?
Awareness is a first step. Know your strengths, be conscious of the list. To work with them you can use consultants, coaches (like myself) or you can try to bring sense to it on your own. You can use the questions below to make a structure around your thoughts. Use those questions to analyze talents one by one from your list:
- What is my TOP 5 and what every talent means?
- Where can I see that I use my talent in my professional life?
- What kind of tasks/projects/work activities are connected to my talent?
- Where can I see that I use my talent in my private life?
- How my talent influences my decision making processes?
- How do I communicate regarding my talent?
- What am I doing with problems that appear regarding my talent?
- What are advantages of having this talent?
- What are disadvantages of having this talent? Where can it do more harm than good? In what situations?
Starting with those questions you can connect the dots between the results of the questionnaire and your real life. It’s not about changing your life now because you have the results. It’s more about finding the way you can use them consciously, make better choices, be aware of their bright and dark sides and how to react more appropriately in different situations. Strengths are for you so you know what serves you and what doesn’t or what kind of tasks you want and don’t want to do.
When I teach about the strengths, I always say: thinking about your TOP 5 is like using the compass. Coming back to the base is the best idea, because it brings us harmony, peace, being sure about our abilities to do something. When you use this knowledge, you can make your life better, because you focus your energy on things that really matter. You don’t waste it on trying to learn something that is really far on your list and you need to invest a huge amount of time, sometimes money or attention to achieve a decent level in it. And at the end of the day, it’s not worth it.
Simplify and edit. It’s my approach to many situations in life. When you focus on the talents you have, it’s easier for you to navigate, because you have the compass in your hand and you know how to use it. Why throwing it to the water?
Isn’t it lazy to only use strengths?
You can think: “okay, but isn’t it lazy to base only on what I’m good at? What about being in a stretch zone, lifelong learning, or working on becoming the best version of ourselves?”.
Focusing on strengths doesn’t mean that you don’t develop. It means that you are more mindful about what you choose to learn and develop within.
I’ll describe it using my own example.
One of my TOP 5 strengths is Achiever.
My Achiever likes to finish things, cross elements from my task list, achieve goals that I set for myself. It is connected to my professional life, health, sports, personal life, development – you name it.
How I grow within this talent? I learn how to simplify and edit, how to set better goals, using OKRs and how to be more adaptive to not get fixed on a goal and forget about the whole world that is around me. I pass this to others as well, so I share what works for me and I encourage people to try different things that might work for them. I learn how to be a better teacher, facilitator and mentor for them so the process of learning is more efficient. It’s a lot in a stretch zone, I need to constantly push myself to take uncomfortable action but it’s how we learn efficiently and with purpose.
The same thing works for me regarding my private life. When I want to achieve something, let’s say I want to run in a 5k race run in less than 30 minutes – I prepare myself to finish this run. I train, I eat well, I take care of my sleep so I regenerate by body well. I learn how to prepare my meals so they have certain amount of every element my body needs, I learn how to manage my sleeping time to help my body recover.
It isn’t lazy to use strengths. It’s mindful and smart. And by saying “no” to things that you don’t want to learn because they are not close to who you are, you train your muscle of focus. You do things at work that are making you sick every time you think about them? See if they are anyhow connected to your strengths. If yes, maybe you just need to stretch a little bit to get new knowledge or tools. If no, maybe it’s a time to have a conversation with your manager and yourself about the future you want to have – in this organization or any other.
The bottom line
Life is too short to focus on what we lack of. As mentioned at the very beginning of the article, it can be more natural to some of us, we were taught that way. But it makes us feel not good enough, smart enough, educated enough, always “getting there”, never “actually there”. It’s exhausting, unhealthy and frustrating to death. We can be smarter about it, better in what we do every single day. It’s a matter of a conscious decision about what we want to do, based on who we are and what are the best areas of ourselves to give it out to the world.
Using your potential will allow you to thrive, to keep your momentum going, to be happy every day. And it will recreate your life so you will be waiting for each Monday to can live through another week with satisfaction, space to grow and change other peoples’ lives.
Isn’t it worth a try?