When I think about all workshops and mentoring processes that I deliver each week, very rarely I don’t talk about it with people. Sooner or later, this is a part of a conversation: whether we work together around communication, feedback, leadership, change or transformation. Today the story about OK-OK Matrix, which another name is Life Positions Matrix.
One of the most important elements of Transactional Analysis framework, a base of building outstanding relationship: professional and private.
What is the Matrix?
The Matrix is a tool that show us four options that consists of set of beliefs, thoughts and feelings we have about ourselves and others. Based on where we are, we have a certain orientation, that becomes a base for our behaviors, ways of reacting on what happens for us: professionally and privately. It doesn’t really matter about which part of our life or work we think, this tool is applicable equally well.
You can take a look on how the Matrix looks like on the simple picture below:
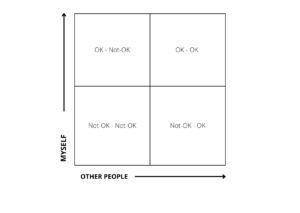
The first axis describes what we think and believe is a truth when it comes to ourselves: who we are (as people in general, but also in each role we have in our life: professionally and personally), what we do, what we are worth because of that etc.
The second axis describes the same elements, but in the context of the external world: it can be another person, a group of people (the entire family, team etc.) or the whole institution (organization, state, the whole political party etc.).
Where we are in the Matrix influences on our mood, mindset, behaviors in different situations, the way we react, how we communicate and make decisions. The first thing is to be aware what kind of dominant tendency we have in going into certain quadrants.
Quadrant 1: OK-OK
OK – OK quadrant is the one that we should aim to be as frequently as possible. This is the space where we are fine, and everybody are fine too. I have good intentions and people have good intentions as well. Of course, not everything and everybody is perfect, but we aim to be the best version of ourselves, we support each other, we share knowledge and work as a team.
This is a place where we have and develop a growth mindset. Thanks to that set of thoughts, believes, convictions and decisions we make base on all that we are successful, happy and build a good life. We see opportunities, abundance, instead of gaps and things we don’t have or know. We reach for more, instead of giving up.
Quadrant 2: OK-Not-OK
OK – Not-OK quadrant appears when you think that you are fine, but others – not so much. Example: ‘I always do everything I can to finish my list of tasks before the day ends, and he never does it. He always works 9-5 and then – regardless of how many things are undone, he just closes his computer and goes home. Ugh, I hate it!’. Or: ‘I’m doing everything I can and this organization? Only requires more and give less and less!’
This place is not healthy for us, since we are going to resent everyone and everything at the end of the day. Even if this is only one person at first, it becomes more and more severe with time. When we are OK and the world not, what we end up with? Hate, resentment, miserable life. I would say that’s not the best place to be, especially in a long run.
Quadrant 3: Not-OK-OK
Not-OK – OK quadrat is a low self-esteem place. We are there when we think that everybody is fine, successful, happy, except for us. A good example can be: ‘Ugh, everybody has somebody, and I’ll die alone with my cats’ or: ‘Everybody can handle their tasklist, and I never have time for anything!’
When we think about ourselves from this position, we are never good enough. Sometimes we choose one work or life role (consciously or not) that we are so bad at that it’s pathetic, sometimes it’s all over the place. It depends on what level of low self-esteem we took with ourselves from our childhood into the adult life. People who are raising us most of the time has good intentions, but the wording and behavior they use is not so good or adequate to those intentions.
Quadrant 4: Not-OK-Not-OK
Not-OK – Not-OK quadrant appears when you think that you suck, but other people too, or you have this belief that the environment / organization / economy / world is bad. Example: ‘My goodness, I am so bad at this, but I cannot learn since I don’t have time for anything in this company. My manager always gives me more to do, the colleagues are not helpful at all, and I need to do everything on my own, even if I have no idea what I’m doing’.
This is the ultimate, negative place, that we operate from the fixed mindset. We don’t see any opportunities, we use fatalistic view of the world, ourselves, our relationships, competences, organization we work with etc. Everything and everyone are bad, there’s no hope for the better.
The Bottom Line
The bottom line here is that we fall out of the first quadrant multiple times every single day. It’s impossible to stay there all the time, since we are triggered by different stressors, we have frustrated motivational needs and that’s why we go into distress. Being in another quadrant than the most optimal one is being conditionally OK: I’m (or the world) is OK only if… I fulfill a certain condition.
The key thing is to recognize when (in which circumstances) we lose our optimal position and what can we do to faster come back to it. Also, what matters is how we behave in relation to others: our employees, team members, supervisors, stakeholders, colleagues, but also in private life: as partners, parents, friends, children to our parents.
Once we are mindful and conscious about it, we can regulate what we do and instead of ruining our relations, we can build them strong and fulfilling.
Regardless of the role in our life and work.




