We all know that. Today is not the day. Too much work, not enough time, too rainy to go outside, too tired to pick up any activity, or just feeling demotivated. And all of the sudden, we realize that several weeks or months passed, and we didn’t do anything. For ourselves, our relations, our health, or our development. All of our beautiful plans and wish lists are buried deep somewhere in a drawer waiting for a better tomorrow.
It is not possible to be super effective, active and positive all the time. Even the most positive and ambitious people have those days when they just want to stay home and be a human burrito. And that’s perfectly fine. But when it is becoming more frequent or appearing regularly, I would encourage you to take a closer look to find out what is going on under the surface.
Here are my personal 5 things that I do when feeling demotivated or having lower level of energy.
1. Find the source of you being demotivated.
Every single thought, emotion, reaction or belief has its root. There are many possibilities that you feel or think in a certain way and all of them are very individual. They are connected to our history, experiences from the past (professional and personal ones), beliefs about ourselves and the world that we gained mostly in our early childhood (most of them until the age of 6) listening to our parents or other people who were raising us and other children. Basically all the people who were some kinds of authority for us at the time or we did seek for their attention, love or acceptance.
From my experience, we remember the best and we have the easiest access to bad beliefs.
Not smart enough.
Not pretty enough.
Not fast enough.
Not thin enough.
Not having the best grades.
Not good enough (meaning nice, not causing any trouble).
(name yours, there are mostly unconscious before we start to think and name them).
And all of those beliefs that we gained in our lives, have an influence on what kind of thoughts we have as adults. And it is connected to what do we think about ourselves and the world that is around us.
Of course the beliefs are just one factor of us being demotivated but as far as I’m concerned, it is the strongest one – I would risk the hypothesis that those beliefs are responsible for 80% of our lower moments. So I encourage you to have a piece of paper (or a Word document) and ask yourself those questions to find the source of your demotivation:
- What I think about myself right now? Am I good enough? Smart enough? Thin enough? Successful enough? Answer yes or no on each of those questions. Check how many of each answers do you have.
- What am I worried about? Make a list, be as specific as you can.
- What have I eaten for the last 3 days? Try to recall as many meals, snacks as you can (including drinks, alcohol, coffee)
- How many hours of sleep did I get for the last 7 days? You don’t need to be specific, use the average number (to find out if it is closer to 4 or 8 hours)
- Did my last 7 days had a structure, certain plan with repetitive elements (i.e. morning routines) or have I just lived them with no specific plan?
- How many meaningful social interactions did I have for the last 7 days? (it can be at work, at home, at the gym, with your friends, family, coworkers etc.)
- How many hours of sports activity did I have for the last 7 days? (you can count actual training sessions but also walks, harder cleaning of the apartment etc.)
2. Fill out the Influence Matrix.
Once you have all the answers on the question above, you can check their position in the Influence Matrix that I’ve created. This is a simple tool that you can use every time when you are stuck, you feel over worried or tired and you don’t know what to do. The matrix will help you to see in a clearer way the connections between having/not having an influence on a certain situation and its importance at the moment. It might seem similar to Eisenhower Matrix but this one uses different variables and its main goal is psychological support, rather than efficiency itself.
Here is the Influence Matrix that you can use to put those elements that you discovered in the previous section.
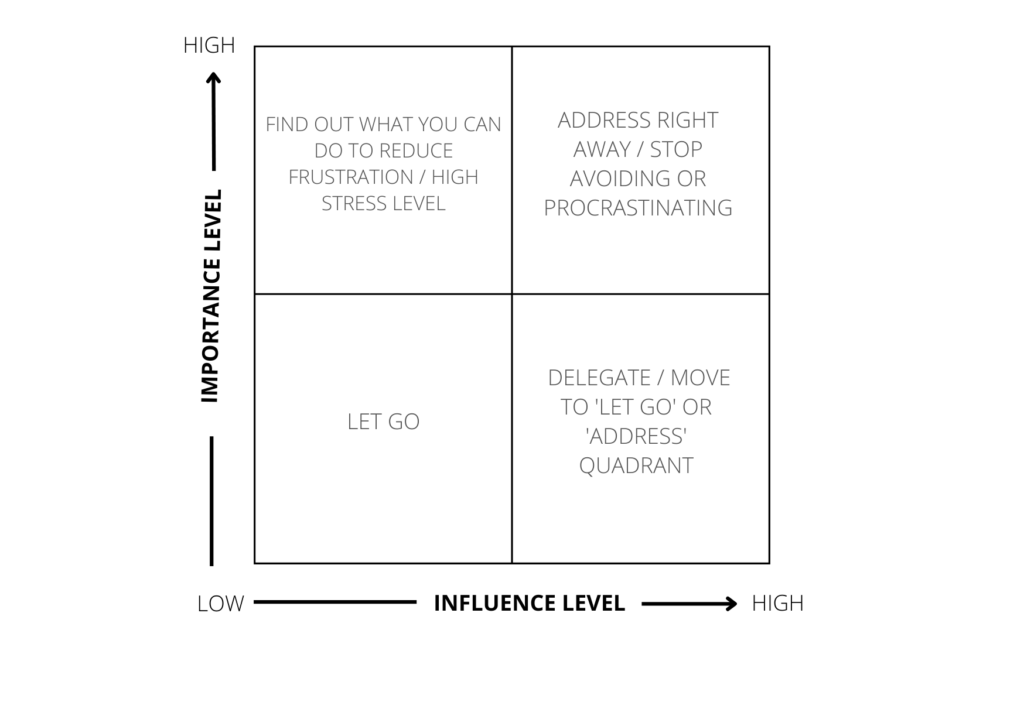
You can draw matrix on your own or you can use ready PDF file that you can download:
Example 1: let’s say you’ve discovered that you worry about high inflation rate. Is it important? Yes. Do you have any influence on that? No, literally zero influence. So you put it in the upper-left quadrant. Then, you need to decide what can you do to reduce the high stress level that is connected to the high inflation rate. Maybe you can check on your home budget i.e. by using an easy excel spreadsheet to see how do you spend your money monthly? Based on that you can temporarily quit on some costs, so you have more financial freedom, and you are less stressed at the end of the day.
Example 2: let’s say you discovered that you did 0 hours of sports activity last week. Is it important? Yes. Do you have any influence on that? Yes. So you put it in the upper-right quadrant. Then, you need to decide what to do to be more active. Pick one thing at the time, i.e. 15-minute walk after lunch every day. If the weather is bad, play a 15-minute workout on YouTube. No excuses!
3. Choose one thing that you have influence on and pick it up right away.
I am a huge advocate of small things. Baby steps. I know from my own experience and from experience of those many people I’ve worked with through the years that we need ambitious goals to achieve extraordinary things. But we also need a simple plan, achievable steps that will keep our internal motivation level high, so we don’t feel exhausted or frustrated that we don’t see effects right away.
That’s why I encourage you to pick one thing at the time. When that one becomes a habit, you can add another one, and then another. Seeing quick results will show your brain that the change is possible and worth the effort.
Choose one thing from your list and pick it up right away. Not tomorrow. Not on Monday. Not January 1st. Right away. Research shows that if we wait for a ‘magical’ moment (like January 1st, for example), it is less probable that we are going to achieve it since it is only ‘a power of this magical moment’. Not very helpful, especially from a long-term perspective.
4. Glue things together to feel less demotivated.
There is an amazing book about building habits: ‘The Power of Habit’ by Charles Duhigg. He writes very specifically about building new habits really closely to the existing ones. This is easier to our brain to glue habits together to keep them stronger and more durable over the time.
Do you want to use dental floss every day? Do it right after you clean your teeth in the evening.
Do you want to meditate regularly? Do it right after your workout (if you already have a habit of working out regularly).
Do want to read more? Prepare a book on your nightstand and right after your alarm rings, sit on your bed and read for 5 minutes (or more, depends on what you need at the moment) before you start your day.
Believe me, sticking habits together will allow you to feel more energized, motivated and satisfied – even if that’s just 5 minutes of reading. It is a start.
5. Check your introvert/extravert energy level.
I learned lately that I need to check my introvert/extravert energy level when I am mapping what is going on with my motivation, vitality and rather positive attitude. Since it influences my efficiency, effectiveness and how I achieve any goal I set up for myself, on personal or professional level, it became an interesting aspect I’ve decided to take a closer look at.
Most of us are somewhere in between the introvert/extravert scale – you can check yourself on the scale below. Where do you think you are right now?
I am an ambivert with a tendency to move into extrovert side. The more extraverted we are, the more energy from the outside of ourselves we need to feel good. From other people at work, our friends, family, people from our community – basically it is all about human energy from the other person. Extraverts also can get their energy from other social situations, i.e. just being on the concert or on a sports event (without talking to anybody) is quite often enough to boost the body and mind. It is all about the energy itself at the end.
The more introverted we are, the more energy we have from the inside of our body and minds. Often, introverts are highly sensitive people, so they need more silence and time alone to feel energetic. And we all need being alone for a bit from time to time. Some of us less, some of us more. But being an extrovert doesn’t mean that we need to be with people all the time.
So when you feel less energetic than usually, check your introvert/extravert energy level. Maybe you are closer to the right-hand side, and you are not leaving your home a lot lately? And maybe you are closer to the left-hand side, and you are pushed to be in a crowd a lot? It can be an important information that will help you decide what to do next to get your energy back.
The bottom line
The bottom line here is that we all have good and bad moments and that’s perfectly fine. I encourage you to think about those elements that have the biggest influence on you: your thoughts, beliefs, habits, people around you (they can be demotivating as well), goals, possibilities or constraints that you have at the moment. Take a closer look on them, decide what really matters and has the biggest influence on yourself and what is totally useless, and it is time to let it go. Choose wisely and be better every single day.




