Great resignation. Employee market. Huge employee gap. The lowest unemployment rate in years.
We see and hear all of that, now maybe even more than ever. Labor market shifts on its own, as well as many organizations needs to rethink how they operate on a daily basis. Regarding their cost and organizational structure, strategy, focus, goals and leadership condition. And while some of them deal with necessary lay-offs, some have quite the opposite challenge: their (mostly) the best employees quit and take another job externally.
Taking into consideration few different studies, approximately 40% of employees think about or act towards a job change. It’s a huge number of people in the organization that for some reasons started to lose or lost their engagement in a current place. What is in top 5 reasons employees quit their jobs?
- Low pay.
- Lack of career opportunities.
- Feeling disrespected at work.
- Childcare issues.
- Not enough flexibility.
Poor management is in top 10 as well, don’t worry. Covid time changed the order a little bit, point 4 and 5 are connected directly to the situation during and post pandemic. More about that further in the article.
So taking all that into consideration – what you can do as a manager so your people don’t quit? Here are 5 things I believe are the most valuable for you and for your people, regardless of the branch, sector, size of the company or space that you work in.
1. Use TRS (Total Reward Statement) before they quit
Nobody teaches managers how to talk about money. We talk about feedback, goal setting, delegating tasks, strategy, team building etc., but when we think about money issues, discussing raises, levels of bonuses we get uncomfortable. It’s connected to two main things.
1. Money is a taboo in a certain culture/country – it’s rude to talk about it openly.
2. We don’t know how to talk about money, especially when we know that there is no space to offer a raise or any additional bonus, so we procrastinate the conversation.
So I say it’s about the time that we start talking about money as openly as about any other aspect of work. And you as a manager can learn how to lead a conversation around it, it’s a competence like any other one.
Total Reward Statement (TRS) is a tool that you can use to talk about money-related subjects with your employees. Most of the time we don’t count everything that employer gives us, we only see the amount of money that appears on our bank account once a month. And in most of the cases it’s so much more than that. By using that you can show your employee what (on a monthly/quarterly or yearly basis) is the total investment in them that organization makes. What else can we show in TRS, besides of a basic salary?
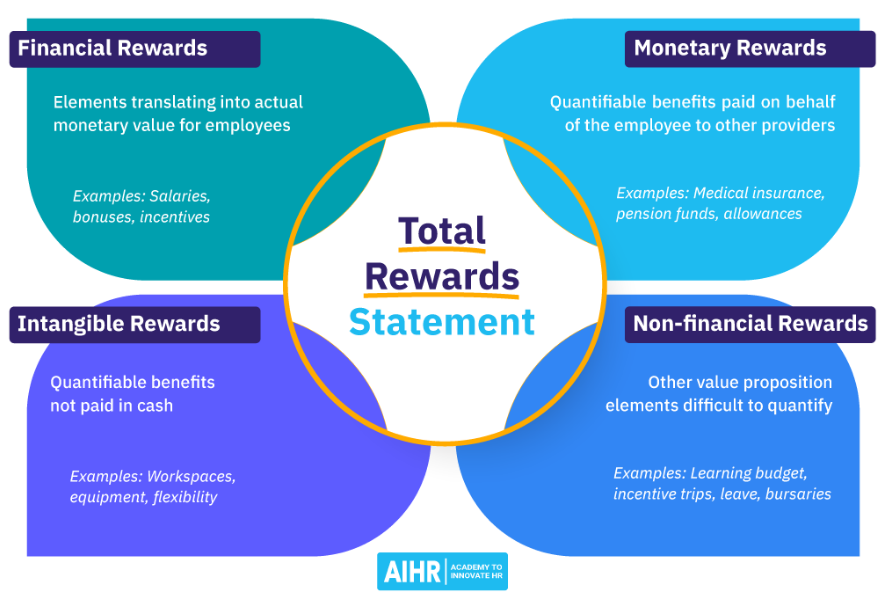
- Bonuses (regular and/or one-time)
- Incentives (i.e. recognition rewards, referral programs, profit sharing/stock options, tuition/trainings/certification programs reimbursement, health and wellness, fun gifts)
- Benefits (i.e. medical insurance, private medical care, pension funds, food in an office, pet health care, concierge services)
- Workspace equipment
- Other learning budget, travels (business and learning-related), extra vacation days
When you make a sum of everything that a certain employee uses (approximately, it’s not about counting every single dollar that organization spend on one person), the conversation around money might starts to look differently. Our employees often don’t see the bigger picture and don’t understand the scale of money that is invested in them. Of course if the organization pays under the market, it’s another story – the question is if you as a manager has any influence to address the pay gap in your team. If yes – do it, as soon as possible to minimize the risk of your people quit in the nearest future. If no – think what other elements in TRS you can use to fill it somehow until the times are better.
2. Co-create career path with your employee
The second one on the list of arguments why people quit is a lack of development opportunities. I hear it a lot. Sometimes this reason is true, but in many cases it’s just an excuse or a lack of knowledge. The first question I ask every single time when somebody comes to me and tells that there are no opportunities for them to grow in this company is: “what did you already try?”.
This question appears as such a strong one that sometimes people don’t know how to answer. They start with: “I tried everything!”. So we talk about what this “everything” means to them. Very often it appears that they didn’t do anything in particular, 80% of the cases didn’t even have a quality conversation with their manager about it! It’s insane.
They didn’t start it and their manager didn’t start it either. Nobody says anything, counting on that the other side WILL GUESS what is at need at the moment. Bs, it’s not going to happen.
So if you are a manager – it’s your job to trigger the conversation about development of your employee. Of course I advise to have a co-creation partnership during the process, not following the idea that you are going to make a plan that your employee will follow. It’s not that engaging when we compare it to actually working together.
Quick question: when was the last time you talked with your employee(s) about their professional/personal development?
Answer honestly, no one’s judging you. First step of every growth is self-awareness.
Plan the space to talk about it, on a regular basis. Ask your employee how often do they need to talk about it, make check points. Don’t guess, don’t assume. Ask questions, listen and be adaptive. Share responsibilities – don’t take everything on your back. The owner of personal development is an employee, always. When they decide to leave the organization, their growth goes with them. It doesn’t belong to you, or the firm. It’s important to say it out loud, to cut the unhealthy and unrealistic expectations. Be honest and transparent about what is possible and what not (at the moment), avoid being cruel though (some managers like to use the “tough love” tool). Our intention is not to scare a person away form taking the responsibility. Our goal should be to encourage them, show them the way, guide them, give feedback on a regular basis. Make it theirs, but assure that they’re not alone in this journey.
3. Use contracting and recontracting as a base of cooperation
The basics about contracting are here, so I’m not going to repeat what the contracting actually is.
When a new employee joins your team, there is a necessary time for both of you to have space to agree on how you want to work together and what you don’t want in this cooperation. It includes:
- structure of work delivery (hours and days, online and onsite work, OKRs, results of work we want to see),
- content (scope of work, responsibilities and decision making; tasks, projects, skills, competencies),
- rules of cooperation (1:1s, team meetings, policies, org structure, team goals, comms and reporting structure, tools we use as an organization),
- psychological aspects of the job (feedback and recognition: frequency, method; hungers and other needs, plans, ambitions, frustrations from the past).
Every time something changes (and let’s be honest – it can be every couple of months), there is a need to come back to the conversation and approach to the recontracting.
Let’s imagine that you hire a person that is 24 years old, no kids and other obligations. He wants to develop his career, earn money to travel, see the world. And after 2 years, he’s having his first kid, he wants to redirect his energy to be a dad and focus on this new journey.
Is the contract that you made 2 years ago valid when circumstances changed like that? Hell no! You need to recontract with him, see which elements of the contract are still up and which of those need to be reframed so the work is done, but he also has time to raise his kid well.
Contracting and recontracting is a useful tool for you so you don’t guess. You don’t waste time on assuming things. And it works both ways. Your employees have transparency, structure that it allows them to be focused on what is really important, without spending it where it just doesn’t. When you skip this, because YOU DON’T HAVE TIME, you lose more time than you can even imagine. And from my experience – as a manager, an HR person, a listener to the organizational voices, a lot of people quit their jobs because they don’t have the clarity. And it doesn’t cost anything, so it’s one of the cheapest things you can implement to avoid the quitting situation.
Use it.
4. Talk about hungers, don’t assume you know everything
It’s connected to the previous one very tightly. We often say we are so busy that we don’t have time to talk to our employees. And like it or not: having conversations with your employees is your main job, if you are a manager. Yes, delivering business too, but you are responsible for other people so business results will be an effect of that cooperation with them. Because without them, you won’t deliver anything.
Structure. Recognition. Stimulus.
Three simple needs all people have. You can save some time on wondering who has what. Everyone has everything, but in a different ratio. Talk to your people. Find out what is their ration of hungers (40 Recognition – 40 Structure – 20 Stimulus? Or maybe 20 Recognition – 70 Structure – 10 Stimulus?). Include in contracting how you are going to cover those needs (i.e. if you have a person who is 40 in Recognition they might need to have feedback meetings once a month, and a person who is 20 in Recognition might need it once a quarter). Of course it differs from person to person. Don’t assume that every employee will be the same. And for the god’s sakes, don’t use the same pattern to your whole team, just because it works with one or two people.
Be smart, don’t waste time. Save time, minimize people who quit by asking questions and actually listen to what your people tell you. You don’t need to do everything they want, it’s not the point. The point is you ask, you listen, you contract with them on what both sides are going to do to keep the momentum going.
That’s how you build a strong, loyal team.
5. Drive stay conversations, not only exit interviews for those who quit
As managers, we often hope for the best. Examples?
Our employees will be engaged.
Teams will deliver, be efficient and effective in what they do.
They will be loyal and don’t quit (at least not right away, without any previous visible signs or warnings).
People will take care of themselves, their development, growth, career paths etc.
And that they will always know what to do, how to do it and when.
It’s funny how we all want results, but don’t really want to put any work in it. It’s a natural human behavior so nothing surprising about it, really. But we need to acknowledge that we have all the influence in the world to change the reality we work in.
As a manager your job is to lead a team. To prevent not to react, whenever it’s possible. Be an owner, not only a consumer of the organization your work within.
That’s why you need to think before things happen. Talk with your people, ask questions, BE MINDFUL on what they tell you. And what they don’t tell you, read between the lines sometime. It’s your job to know how to do it.
Stay conversation is a tool with a preventive function, so you can do something before people will start looking for another job. Or before the new job is going to start looking for them (especially when they are experts in what they do). During this meeting you create a space to talk about what works and what doesn’t. What bothers your employee and what helps them grow and work efficiently. What kind of chances and risks this person see, regarding your work together as a team and/or as an organization.
It’s a space for your employee to tell what you can do as a manager (directly or indirectly – sometimes the second option is even more valuable) so they don’t quit. It’s as simple as that. You can find out more about the subject using additional resources – find a structure that will work for you. It can save you a lot of time, money, energy, unnecessary negative emotions and guilt. I guess it’s worth the time invested in this conversation.
The bottom line
You can say: “I don’t have time” or “I don’t have money to give raises”. You can say: “I don’t have any influence on other people”.
Or you can cut the bs and start doing your job. Because it’s only up to you how you use your time, what kind of decisions you make, how well you know your people and how often you have a real quality conversation with them. Use your position, your role and scope of influence you have and be a manager that people don’t quit.
At least not right away after you recruit them and not in an unhealthy frequency. Remember that there is a healthy attrition as well. Sometimes we need to have new blood in our teams, sometimes some team members are not longer a fit to where we are as a team or a company. But when you can do something and you want, do it. Don’t wait until somebody comes to you with a termination letter and then you start thinking about responding to it.
90% of the time it’s too late.




