What do you think about the people who are always extremely motivated? Do you think that’s true? Possible? Or they are just show this side of themselves to the external world and the true is that they are miserable, lonely, they hate their jobs and only tell lies about their golden motivation?
What if I tell you that being highly motivated through most of your life is possible and achievable? That a lot of people in your closest environment – at work, home, local community is already doing it? What if I tell you that you can do it on your own, just by switching few small things in your life?
Here’s another chunk of Transactional Analysis to add to all you’ve already got to know after reading previous pieces of the series. Let’s go with Motivation today.
Is Motivation even a real thing?
When we think about motivation, we look for a miraculous source of energy, potential or power that’s going to push us to do extraordinary things. It can be true, but we need to remember that there is no source on this planet that is infinite. So what if we operate only on the highest level of optimism and energy, and we don’t do anything when this energy is lower? We succeed only from time to time and it’s not something we should seek for.
Motivation is just one aspect of being successful, achieving all those things that you want. But we can be smarter about it, discover what are the real aspects of your work, life, relations or health that motivate you to stay on truck, to do things, to make good decisions. And stick to that to be our best selves most of the time – instead of waiting for the perfect circumstances. Where to start?
Let’s start with Susan Fowler.
Susan Fowler’s Spectrum of Motivation
Susan Fowler is one of the foremost experts on motivation and personal empowerment. She worked with a huge number of individuals, managers, teams and organizations to find out what is the truth about the motivation itself.
Susan’s Story
Her book “Why Motivating People Doesn’t Work… and What Does” is one of the best books in the field I’ve ever read, I strongly recommend it to anyone, regardless of the age, maturity, years of experience or place of living.
There is one story which sticked with me since the first time I’ve heart this during my TA training. One time a manager came to Susan and said: “you know what, my team is so demotivated! What can I do to motivate them?”. She asked him a question in response to it: “do they come to work every day?”. “Yes, they do”. “Oh right, so they are already motivated. The real question is HOW”.
It is nobody’s job to keep the other person motivated. External motivators are short-lived, sometimes they address only imaginative needs and what’s the most important – we remember about them only for a couple of minutes (the first moment of euphoria). And that’s it. I would make one step further to what Susan asked this manager about and say this: “how can we find out what are our REAL internal motivators that keep our momentum going?”.
Spectrum of Motivation Model
To better understand how people think, act, make decisions and keep themselves motivated, here is Susan Fowler’s concept of Spectrum of Motivation.
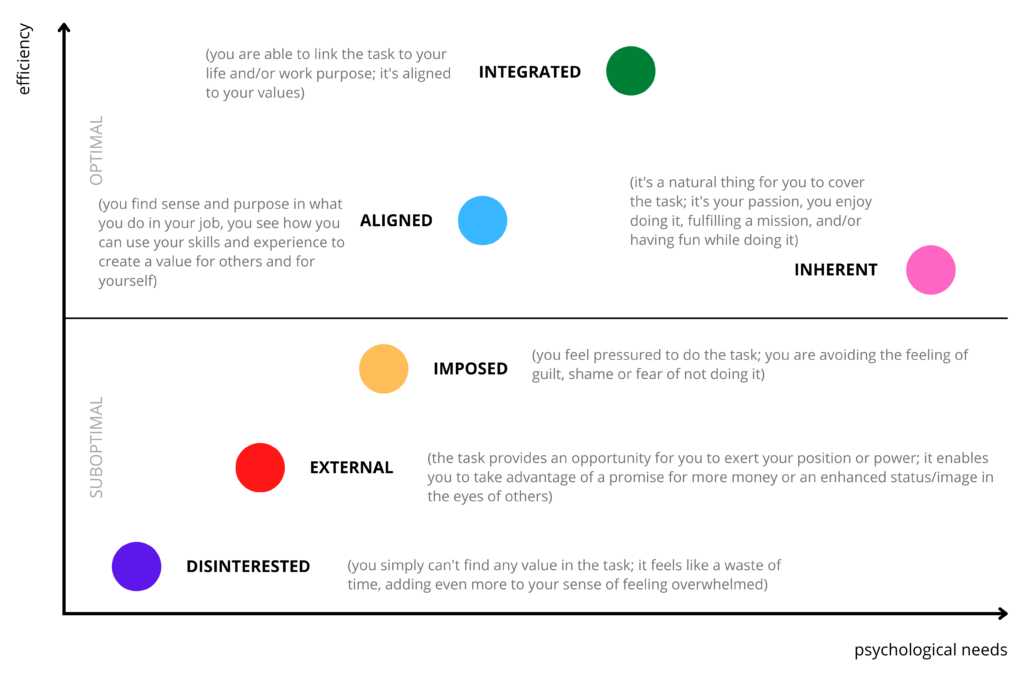
2 axes make this concept alive. The first one covers psychological needs. Regarding Susan Fowler, psychological needs are described by 3 main things:
- Autonomy. It’s about having an influence on what is happening around us, an ability to be independent and to create things, to bring value to the table.
- Competences. It’s about learning new things and unlearning the old ones, in order to be efficient and effective, as well as taking responsibilities for what we do and/or what we promise to others and to ourselves.
- Relations. It’s about having purpose and getting support when needed, to be appreciated and seen as a person, to have others in the right amount and the right time we need them.
The second axes is about efficiency – doing things right, but also thinking about it in connection to effectiveness – doing the right things.
By structuring those descriptors, it would be easier to understand the whole model, which is divided into 2 spectrums: Suboptimal and Optimal.
There are 3 levels of Suboptimal motivation:
- Disinterested. In this state we feel disconnected from what we do. Completely demotivated, without even one spark of energy or sense of purpose. We often feel burned out, overwhelmed, sometimes even depressed, spending time mainly on scrolling through social media or watching another series. This is the stage with the lowest efficiency and the lowest level of coverage the psychological needs.
- External. In this state we can do things, but only when we’ll get something in exchange. “Yes, I can train the new employee – but how much money will I get? Yes, I can run this project – but where my name will be put in internal and external communication? Yes, I can support this initiative – which parking spot in front of the headquarters will I get?” External motivation is short-term, it can boost a certain behavior, but it won’t keep it for long (since there is always going to be greed to have more). This is a stage where the efficiency is higher, but the psychological needs are not covered very well (they can be for a moment, but it is very fleeting).
- Imposed. In this state we do things because we are afraid of being punished, pointed out during a team meeting (ha-ha, look at John – he didn’t hit his target AGAIN!) or we don’t want to feel guilty of “not being helpful”. So we do things – even if we don’t like them, we need to work over hours or on the weekends to complete everything what’s needed. The job is done at the end of the day, but we are in a constant fear or guilt. This is a stage where the efficiency can be quite high, but psychological needs are covered only in the moments where we are not punished.
Those 3 levels are not something we should seek. If you feel that you might be in one or two most of the time, take a closer look on the next part of the model to see what other way the life can be.
And 3 levels of Optimal motivation:
- Aligned. In this stage, we understand the goals we have and how they contribute to the bigger picture of the organization (if work-related) or our life in overall (if personal-related). We see how they are linked together, we connect the dots and acknowledge what kind of value we can create for ourselves and/or for others. This is the point where we are efficient, and our psychological needs are covered really well.
- Integrated. In this stage our values are integrated with the values of the organization and/or other people. We feel that what we do has a purpose, be believe in the cause and we focus our energy on the thighs that really matter. This is the point of the highest efficiency and a very high level of covering psychological needs.
- Inherent. In this stage, we sometimes forget about the world that is around us, we can lose track of time. It’s because we feel passionate about what we do, it is a pure pleasure to create something, be innovative, work on what brings a real change, joy, fun or just make people happy. This is the point of the highest coverage of psychological needs, but because sometimes we lose track of time while being so passionate, we can miss deadlines (that’s why it’s not in the highest place on the efficiency axis).
Use all the things you already know to boost your Motivation
Use all the knowledge that you got from this article to answer the following questions:
- Where am I on the Spectrum of Motivation Model (choose 1-2 dots where you are most of the time)?
- If Suboptimal: what is happening (or what happened) that I’m there? What do I have an influence on to change it? What actions do I procrastinate or don’t do at all that can be helpful to change my place?
- If Optimal: what helps me to be there? What can I do to stay there as long as possible? How can I develop even more to keep the momentum going?
- What one thing can I change to become the best version of myself as a professional/person/partner/friend/parent?
- Whom can I ask for more feedback about myself, since maybe I don’t see the whole picture?
Use those questions, stay curious. Find out what is really underneath the surface, be honest with yourself – it’s the only way to move on and have a better life.
If you’re stuck, don’t know what do to, where to start, you can always find a person who can help you. HR, coach, mentor, therapist, but it can also be a friend, a family member or a neighbor. Sometimes it helps just to talk to somebody and say some things out loud. When we say and hear things, especially when they are difficult or hard, bringing us shame or a feeling of guilt, it can have a therapeutical outcome.
Try it out, find the source of your true, optimal motivation and improve yourself to stay as long as possible in that area. It’ll influence the quality of your work, relations, sleep, health and balance in overall. Connect the dots, see how they work together and be an owner of your life.